CHAIN OF INFECTION
Epidemiology involves knowing how disease spreads and how it can be controlled. Infection can only spread when conditions are right. This set of conditions is referred to as the chain of infection, which consists of six links. When all the links are connected, infection spreads (APIC, 2023).
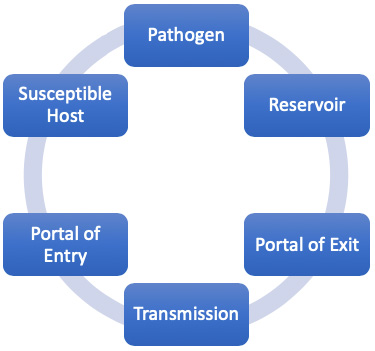
Chain of infection.
(Source: Wild Iris Medical Education, Inc.)
- Infectious organisms can be bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites.
- A reservoir of an infectious agent is the habitat where the agent normally lives and grows. Reservoirs may be dirty surfaces and equipment, humans, animals and insects, or soil. In the case of bloodborne infectious diseases, humans are generally the reservoirs.
- The portal of exit is the path by which the infectious agent leaves its host. This can occur through open wounds or skin, the splatter of body fluids, aerosols, or needle or other sharps contamination.
- Means of transmission is the mode by which the infectious agent is transmitted from its natural reservoir to a susceptible host. Transmission can occur by a mode that is direct (e.g., OPIM exposure from the reservoir patient directly to exposed nonintact skin or mucous membrane of the host) or indirect (e.g., needlestick).
- The portal of entry refers to the way in which the infectious agent enters the host. The portal of entry must provide access to tissues in a way that allows the infectious agent to multiply and thrive. Portal of entry for bloodborne pathogens can include broken or punctured skin, incisions, mucous membranes, and across the placenta to fetus.
- The final link is the vulnerable host. Susceptibility of a host depends on many factors, including immunity and the individual’s ability to resist infection.
(APIC, 2023)
By breaking any link of the chain of infection, healthcare professionals can prevent the occurrence of new infection. Infection prevention measures are designed to break the links and thereby prevent new infections. The chain of infection is the foundation of infection prevention.