HIV/AIDS Training
CONTACT HOURS: 3
Copyright © 2023 Wild Iris Medical Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
LEARNING OUTCOME AND OBJECTIVES: Upon completion of this course, you will have increased your knowledge of HIV/AIDS in order to better care for your patients. Specific learning objectives to address potential knowledge gaps include:
- Discuss HIV and the epidemiology of HIV infection in the United States.
- Explain HIV/AIDS etiology.
- Summarize the risk factors for transmission of HIV.
- Describe HIV testing and counseling.
- Describe the clinical manifestations of HIV.
- Identify antiretroviral therapy and patient care management guidelines for HIV/AIDS.
- Summarize preventive and control measures for HIV/AIDS.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Introduction
- HIV/AIDS Etiology and Pathogenesis
- HIV Transmission and Risk Factors
- HIV Testing and Counseling
- Clinical Stages and Manifestations of HIV and AIDS
- Antiretroviral Therapy (ART)
- Patient Care Management
- HIV Prevention and Risk Reduction Strategies
- Conclusion
- Resources
- References
INTRODUCTION
The HIV/AIDS pandemic has now been with us for over four decades, and in that span of time, at least 32 million lives have been lost. The pandemic continues to expand in Eastern Europe, Central Asia, the Middle East, and North Africa (Beyrer, 2021).
HIV/AIDS in the United States and Dependent Areas Today
As of 2021 in the United States and its six dependent areas, there were more than 1.2 million people living with HIV. In 2020, 30,635 people received an HIV diagnosis—a 17% decrease from the previous year. Among 28,422 persons with HIV infection diagnosed during 2020 in the 46 jurisdictions with complete reporting of laboratory data to the CDC, viral load was suppressed in 67.8% of persons within 6 months of HIV diagnosis.
In 2020, there were 18,489 deaths among adults and adolescents diagnosed with HIV, attributable to any cause, including COVID-19.
Among those who received an HIV diagnosis during 2020, more than 1 in 5 persons (21.6%) received a late-stage diagnosis (AIDS). The highest percentages of late-stage diagnoses occurred among:
- Persons ages 55 and older (37.1%)
- Asians (27.7%)
- Females (23.2%)
The lowest percentages were among:
- Transgender men (5.0%)
- Persons ages 13–24 years (9.1%)
- Black/African Americans (20.0%)
- Native Hawaiian/other Pacific Islanders (20.0%)
The percentage among injection drug users were:
- Females (78.1%)
- Males (77.8%)
(CDC, 2022a)
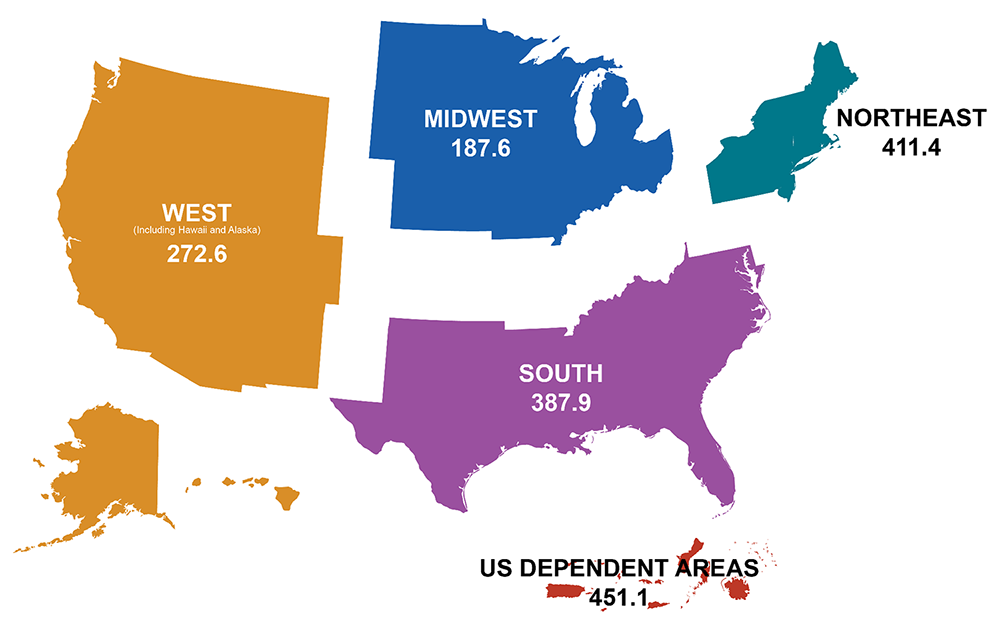
Rates of people with diagnosed HIV in the United States and dependent areas by region of residence, 2021, per 100,000 people. (Source: CDC.)